Overview
We all are quite familiar with what diarrhea is. It is the common occurrence of watery and loose stools. However, it is still a serious disorder. This blog contains all the information you need to know about diarrhea. The following 5-minute read will enlighten you about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diarrhea.
What is Diarrhea?
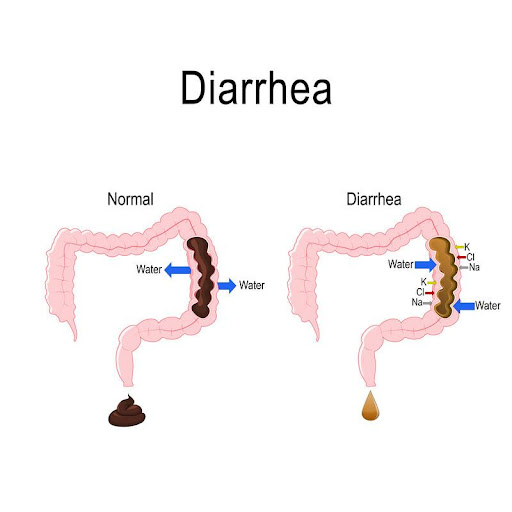
Diarrhea is a common condition of having a loose and watery bowel movement (stools). In this condition the frequency of bowel movements increases. It is usually not considered a life-threatening condition, especially in adults. However, it should be taken seriously when in children as it can be life-threatening, if not treated immediately.
It is important to note that diarrhea that persists for more than 2 weeks might be an indication of some other underlying disease. These conditions may include irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or celiac disease.
Diarrhea claims the lives of 525,000 children under the age of five per year, or around 2195 every day. This is the second largest cause of mortality for children under the age of five and accounts for 8% of all fatalities.
Symptoms of Diarrhea
An individual with diarrhea may have different symptoms depending upon the severity and the causative agent of the disease. A person having diarrhea may experience all of the signs together or may experience only a few. However, the most prominent indication of diarrhea is loose, frequent, and watery bowel movements.
During mild diarrhea, the symptoms you may experience include;
- Urgent bowel movement
- Discomfort in stomach
- Bloating in the abdomen
- Nausea
The symptoms of severe diarrhea include;
- Severe cramps in the stomach
- Fever
- Dehydration
- Loss of weight
- Vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Mucus in stool
When to call the doctor?
There are different severe symptoms of diarrhea in children and adults. You should consult a doctor if you are an adult and are experiencing the following symptoms;
- Diarrhea lasting for two or more days
- Dehydration
- Severe abdominal cramps
- 102° F fever or above
- Blood in stool or stools of blackish color
Diarrhea in children requires immediate care as it can lead to dehydration within a matter of hours. Consult a doctor if the condition of your child does not improve within a day. The signs to notice in children include;
- Blood in stool or stools of blackish color
- Dehydration
- 102° F fever or above
Serious symptoms of dehydration
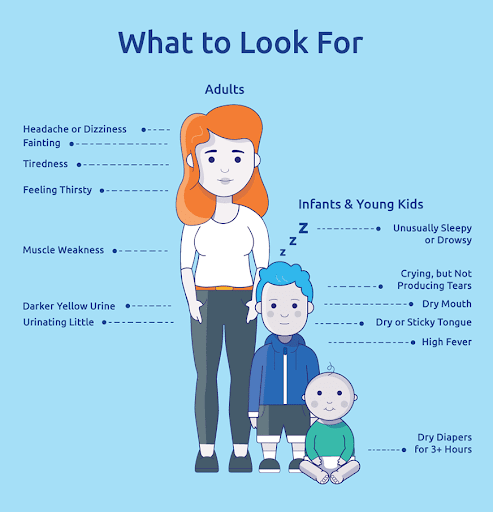
The main complication that is involved with diarrhea is dehydration. With the watery bowels in diarrhea, the body loses more water than its intake leading to dehydration. The symptoms of dehydration also vary among adults and children. Signs of dehydration in adults include;
- Decreased urination
- Dry mouth and skin
- Increased thirst
- Darker urine
- Tiredness, weakness, lightheadedness
Signs of dehydration in young children and infants include;
- Dry mouth and tongue
- 102° F fever or above
- Tearless crying
- Lack of energy
- Irritability and lack of response
- Decreased urination and dry diapers for more than three hours
Complications accompanied by diarrhea
Diarrhea itself is usually not life-threatening. However, the complications it is accompanied by can turn out to be lethal. Dehydration (when your body loses a lot of water), electrolyte imbalance (loss of sodium, potassium, and magnesium), and renal failure are all effects of diarrhea that have serious consequences.
Causes of diarrhea
For the effective treatment of diarrhea in both children and adults, it is important to know its causative agent. The general causes of diarrhea include the following;
Viruses
Norwalk virus (also known as norovirus), enteric adenoviruses, astroviruses, cytomegaloviruses, and viral hepatitis are some of the viruses that can cause diarrhea. Rotavirus is another significant and typical cause of diarrhea in children. Coronavirus also causes GI symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Parasites and bacteria
Parasites and bacteria can be significant causes of diarrhea. Dangerous bacteria like E.coli can enter the body via food and can cause diarrhea. Clostridioides difficile is another significant cause of diarrhea. It is commonly known as C. diff.
Medications
Antibiotics are used to kill harmful bacteria inside the body to treat infections. However, this may result in the eradication of useful bacteria. The lack of useful bacteria results in digestive disorders including diarrhea. Medications used in the treatment of cancers may also cause diarrhea.
Intolerance to lactose
The sugar present in milk is called Lactose. In the absence of lactase, the enzyme used to digest lactose, lactose intolerance is developed which also causes diarrhea. Because levels of lactase decline as you age, lactose intolerance may worsen with aging.
Synthetic sweeteners
Some otherwise healthy individuals may get diarrhea after consuming the artificial sweeteners sorbitol, erythritol, and mannitol, which are non-absorbable sugars used in chewing gum and other sugar-free goods.
Surgical procedures
Diarrhea can occasionally result from the removal surgeries of the gallbladder or part of the intestine as such procedures disturb normal digestion.
How is diarrhea diagnosed?
To diagnose diarrhea, the doctor will take an elaborate medical history. This will include the current medications you are using, along with an account of what you have consumed recently. The next step will be a physical exam to determine symptoms of dehydration or stomach cramps.
To determine the exact cause of diarrhea, the doctor might conduct a few blood tests. If the doctor is sensing that the cause of diarrhea is a parasitic or bacterial infestation, then a stool test might also be required.
Occasionally, doctors opt for colonoscopy to diagnose the cause of diarrhea. Colonoscopy is a medical procedure in which the doctor inspects the insides of the colon using a small camera and light attached to a thin and flexible tube. The apparatus of colonoscopy can also be used to extract sample tissues from the inside of the colon. The doctor might also conduct another test called sigmoidoscopy to examine the lower colon.
Treatment of diarrhea
There are several ways to cure diarrhea. These treatments vary according to the condition of the patient.
Natural ways to treat diarrhea
In case you are experiencing acute or mild diarrhea then it can be managed at home without requiring any medication. The most important step to treating diarrhea naturally is to combat the dehydration caused by it by consuming plenty of water. Diluted and pulp-free fruit juices can help you overcome the electrolyte imbalance caused by diarrhea. ORS (Orally Rehydrated Solution) can also be used to overcome dehydration and electrolytic imbalance. You can make ORS easily at home by dissolving six teaspoons of sugar and one teaspoon of salt in five cups of water.
Changes in diet can also be a simple and beneficial cure for diarrhea. Decreasing caffeine can help as caffeinated drinks including coffee, green tea, chocolates, and diet sodas have a slight laxative impact. Cabbage, beans, carbonated beverages, etc. should also be avoided as they tend to increase gas production in the digestive tract which can increase further discomfort during diarrhea. Dairy products should also be avoided as diarrhea can increase lactose intolerance in individuals.
Food items that can help to treat diarrhea naturally include low-fiber foods. These foods help to solidify the loose, watery stools. Low-fiber foods include potatoes without skin, white paste, white rice, noodles, bananas, chicken without skin, etc. BRAT (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, and Toast) diet can be used to limit the intake of greasy, and fatty foods.
Over-the-counter drugs
The majority of the time, diarrhea can be treated at home. You’ll typically feel better fairly quickly if you use an over-the-counter medication like bismuth subsalicylate (commonly available in Pakistan with the brand name of Kaopectate or Pepto-Bismol) and Loperamide (commonly available as Imodium). It is important to go through the instructions given on the packaging and avoid over-dosage. If the symptoms persist for longer than 5 days, you must consult the doctor.
Also, it is important to call the health care provider of your child before administering any over-the-counter drugs to them.
Ways to treat persisting diarrhea
Over-the-counter drugs aren’t always the answer, though. If you are noticing symptoms like fever or blood in your stool accompanied by diarrhea, then you require serious medical attention.
In case you have persisting diarrhea for more than five days, your doctor will look into the underlying cause of the problem and will treat it. This could entail a variety of therapeutic approaches, such as:
Antibiotics
Antibiotics or other medications are preferred by doctors to treat diarrhea if its causative agent is an infection or a parasite.
Medication for a particular ailment
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, microscopic colitis, or bacterial overgrowth are just a few of the other medical diseases that can cause diarrhea. Diarrhea is typically under control after these causative agents are treated.
Probiotics
Composed of collections of beneficial bacteria, probiotics are occasionally used to treat diarrhea by re-establishing a healthy biome. Before beginning to use a probiotic or any other form of supplement, always see your doctor.

Preventions of diarrhea
Following are the ways you can prevent diarrhea
Maintain good hygiene
By maintaining good hygiene, you can prevent diarrhea to a great extent. Hand hygiene should be maintained especially before and after making food, handling raw meat, visiting the restroom, diaper-changing, sneezing, eating, coughing, and blowing your nose. A habit of washing hands for 20 seconds should be developed.
In case of unavailability of water or soap, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. As you would use a hand lotion, dispense the hand sanitizer evenly over the front and back of both hands. Utilize a product that has at least 60% alcohol by volume.
Get vaccinated
Inquire your child’s doctor about the recommended vaccinations for diarrhea. Proper vaccination can safeguard your infant from rotavirus which is the most widespread virus causing diarrhea in infants.
Keep an eye on your consumption
It is important to keep an eye on what you are consuming especially if you are at someplace that is at a higher risk of diarrhea. Prefer eating fully cooked meals and avoid raw or undercooked foods. Avoid alcohol and caffeine as they can increase dehydration and bowel movements. Also, guarantee that you are consuming safe, clean, and preferably bottled water.
Consult your doctor regarding antibiotics
Ask your doctor about antibiotics before you travel if you plan to spend a lot of time in a place that lacks proper sanitation, especially if your immune system is already compromised.
Verify any travel advisories
Disease alerts are issued on a webpage for travelers’ health that is maintained by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If you intend to travel, look there for precautions and risk-reduction advice.

Conclusion
Diarrhea is a common condition that we come across every now and then. However, it holds serious impacts if not treated timely. Knowing the symptoms and causes of diarrhea, you can ensure suitable treatment for yourself and your children. There are various options available to treat diarrhea, still, it is important to treat children with caution. By maintaining proper hygiene, getting vaccinated, and practicing mindful eating, diarrhea can be prevented.